Infrared cameras are powerful tools for detecting heat patterns, identifying faults, and enhancing safety across a wide range of industries. Whether you’re monitoring electrical systems, inspecting mechanical equipment, or detecting gas leaks, thermal imaging delivers real-time insights that improve operational efficiency and prevent costly failures. But before diving into an infrared solution, there’s a key decision to make: should you go with a fixed infrared camera or a handheld one?
Both options offer significant advantages—but the right choice depends on your specific application, workflow, and goals. In this article, we’ll break down the core differences between fixed and handheld infrared cameras, explore their ideal use cases, and help you determine which solution best fits your operational needs.
Understanding the Basics
Handheld Infrared Cameras
Handheld infrared cameras are portable devices operated by technicians or inspectors. They’re used to scan equipment, buildings, or assets on the move and provide immediate thermal images. These cameras are typically battery-powered and designed for use in the field or in environments where flexibility and maneuverability are critical.
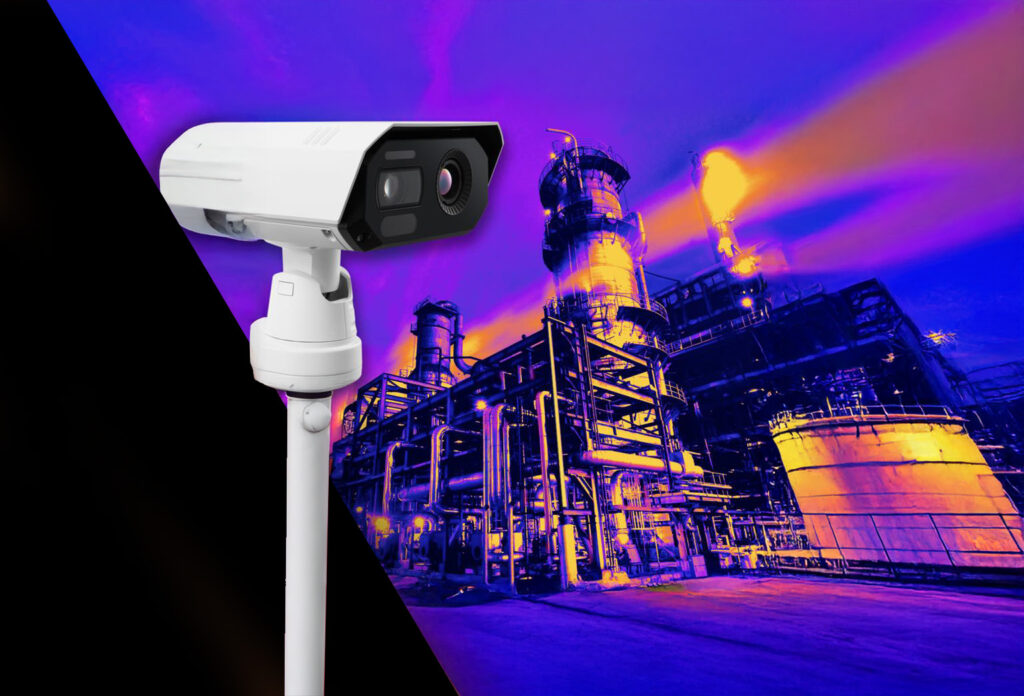
Fixed Infrared Cameras
Fixed infrared cameras are permanently installed and mounted at a specific location, often integrated into a broader automation or monitoring system. These cameras provide continuous thermal surveillance, capturing temperature data 24/7 without the need for manual operation. They are ideal for monitoring critical infrastructure or high-risk areas where constant observation is required.
Comparing Features and Functionality
| Feature | Handheld Infrared Cameras | Fixed Infrared Cameras |
| Mobility | Highly portable, flexible | Stationary, not portable |
| Operation | Manual, technician-operated | Automated, remote monitoring |
| Use Cases | Inspections, troubleshooting | Continuous monitoring, early warning |
| Integration | Standalone or semi-integrated | Fully integrated with IoT, SCADA, alarms |
| Data Collection | On-demand snapshots or video | Real-time, ongoing data streams |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost | Higher investment, long-term ROI |
| Training Required | Basic thermography knowledge | Advanced integration and system knowledge |
When to Choose a Handheld Infrared Camera
Handheld cameras are best suited for routine inspections, on-the-go diagnostics, and fieldwork. Their portability allows technicians to move between assets, focus on problem areas, and capture thermal data as needed. These cameras are often used in:
- Electrical Inspections: Quickly identify overheating wires, transformers, or switchgear.
- Mechanical Maintenance: Detect wear and tear in bearings, motors, and pumps.
- Building Diagnostics: Find insulation gaps, water damage, or HVAC inefficiencies.
- Safety Checks: Inspect equipment before startup or after maintenance.
- Emergency Situations: Rapidly assess conditions in response to alarms or unexpected shutdowns.
Handheld units are also ideal for smaller operations or companies with tight maintenance schedules. They allow staff to conduct targeted inspections without the cost of a full-scale thermal monitoring system.
Benefits of handheld infrared cameras:
- Lightweight and easy to carry
- Intuitive user interfaces
- Quick deployment
- Versatile for multiple job sites
- Lower initial investment
However, because they require manual operation, handheld cameras don’t provide the constant surveillance needed for mission-critical systems.
When to Choose a Fixed Infrared Camera
Fixed infrared cameras are designed for automated, continuous monitoring of high-value or high-risk assets. Once installed, they provide real-time thermal data to alert operators to abnormal conditions—before a failure or hazard occurs. These systems are best for:
- Substations and Power Grids: Monitor SF6-insulated equipment and detect electrical faults 24/7.
- Manufacturing Facilities: Track temperature trends across machinery to prevent overheating and downtime.
- Oil & Gas: Support Leak Detection and Repair (LDAR) programs by continuously identifying methane or VOC emissions.
- Critical Infrastructure: Safeguard transformers, turbines, and switchgear with automated alerts.
- Remote Sites: Offer thermal surveillance in areas difficult or dangerous to access.
These cameras are often integrated with SCADA, IoT platforms, and alarm systems, allowing data to be viewed and acted on remotely. They’re invaluable in applications where any downtime can result in safety risks, environmental violations, or revenue loss.
Benefits of fixed infrared cameras:
- Continuous, real-time monitoring
- Integrated data collection and analytics
- Early warning systems for anomalies
- Remote operation in hazardous or distant areas
- Better suited for automation and scalability
While more expensive up front, fixed cameras offer a strong return on investment in high-volume, high-risk, or high-value environments.
Hybrid Use Cases
In many situations, businesses benefit from using both fixed and handheld infrared cameras. For example:
- A power plant may install fixed thermal cameras at key substations to monitor for faults continuously, while also equipping field technicians with handheld cameras for periodic checks and maintenance rounds.
- A manufacturing facility might use fixed cameras to automate detection of critical failures, while handheld devices are used for quality control and inspecting new installations.
- A refinery using fixed cameras for environmental compliance (such as methane detection) could deploy handheld units during shutdowns or when exploring areas beyond the reach of the fixed system.
The synergy between fixed and handheld technologies ensures broader coverage, flexibility, and redundancy.
Questions to Ask Before Choosing
To determine the right fit for your organization, consider the following:
- What are you monitoring?
- Stationary, mission-critical assets? → Fixed
- Mobile, broad, or varied assets? → Handheld
- Stationary, mission-critical assets? → Fixed
- How often do you need data?
- Continuous data stream or 24/7 surveillance? → Fixed
- Periodic inspections or maintenance checks? → Handheld
- Continuous data stream or 24/7 surveillance? → Fixed
- What are your staffing capabilities?
- Dedicated monitoring team? → Fixed
- Field technicians on the move? → Handheld
- Dedicated monitoring team? → Fixed
- Are you working in hazardous or remote areas?
- If human presence is risky or impossible, fixed cameras reduce exposure and enhance safety.
- If human presence is risky or impossible, fixed cameras reduce exposure and enhance safety.
- What’s your long-term goal?
- Compliance, automation, predictive maintenance? Fixed cameras integrate well into smart monitoring systems.
- Flexibility, lower cost, on-demand analysis? Handheld cameras deliver agility and fast diagnostics.
- Compliance, automation, predictive maintenance? Fixed cameras integrate well into smart monitoring systems.
The Right Infrared Solution Drives Better Results
Whether fixed or handheld, infrared cameras offer unique advantages that can transform the way your organization approaches safety, maintenance, and compliance. The key is understanding your environment, objectives, and technical needs.
Looking to deploy the best infrared solution for your operation? ICI’s experts can help you assess your site, evaluate your needs, and recommend the right camera system—handheld, fixed, or both.
Contact ICI today to explore how thermal imaging can optimize your safety, efficiency, and ROI.