Introduction
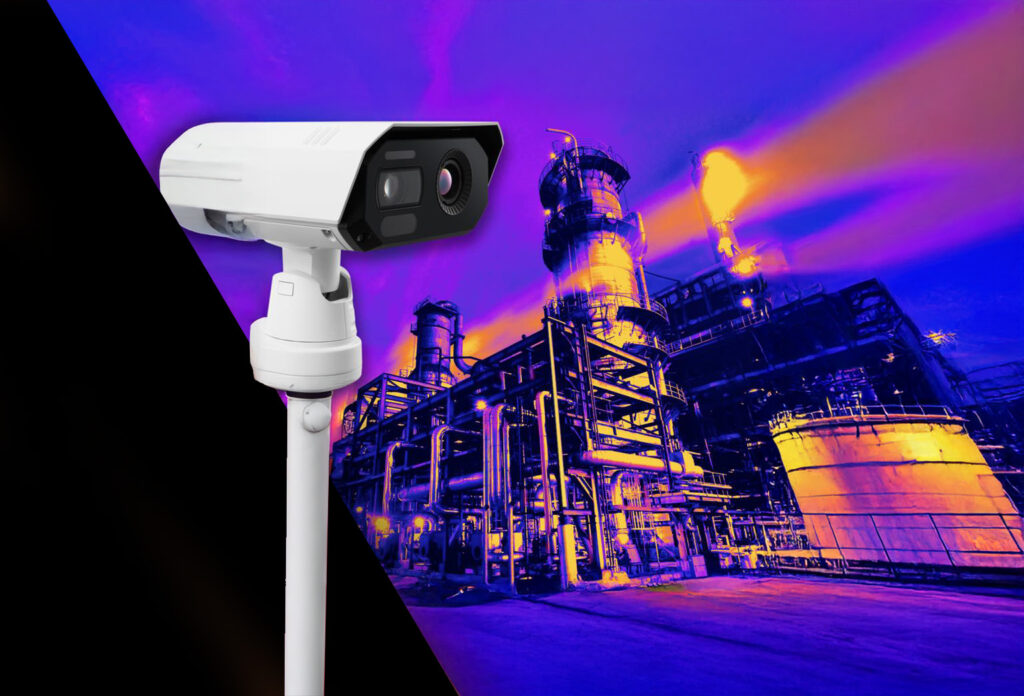
Thermal imaging has become an essential tool across various industries, from industrial maintenance to search and rescue operations. It allows professionals to detect temperature variations and identify issues that might otherwise go unnoticed. But what happens when these cameras are taken into extreme environments—where heat, moisture, dust, and other harsh conditions threaten their performance?
Using thermal imaging in rugged settings requires more than just turning on a camera and pointing it at a target. To get accurate readings and ensure your equipment lasts, you need to follow best practices designed for extreme conditions. Whether you’re in an arctic tundra, deep in a mining tunnel, or working in a chemical plant, understanding how to protect and optimize your thermal camera is crucial.
Let’s explore how to get the most out of thermal imaging in even the toughest environments.
Why Harsh Environments Pose a Challenge for Thermal Cameras
Before we dive into best practices, it’s important to understand why harsh environments create problems for thermal imaging.
Imagine trying to get a clear picture in the middle of a dust storm. That’s essentially what happens when fine particles coat your camera lens, reducing image clarity. High humidity can cause condensation inside the camera, affecting accuracy. And if you’re dealing with extreme temperatures, your camera itself might struggle to function properly.
Thermal cameras are built to withstand a lot, but like any tool, they need to be handled correctly to perform at their best.
Choosing the Right Thermal Camera for Extreme Conditions
Not all thermal cameras are created equal, and picking the right one for the job makes all the difference. If you’re working in an industrial setting with heavy dust and debris, a standard camera won’t cut it. You need something with a high Ingress Protection (IP) rating to prevent dust and moisture from interfering with the internal electronics.
For environments with temperature extremes—like an oil refinery or a frozen tundra—look for a camera with an extended operating temperature range. Many advanced models are designed to withstand temperatures well beyond what a human could tolerate.
And if your job involves working in rugged terrain or high-impact areas, shock resistance is a must. A camera that can’t survive a fall or withstand vibrations from heavy machinery won’t last long in the field.
Protecting Your Thermal Camera in the Field
Even the most durable thermal cameras require proper care. Here’s how to keep them in top shape while working in harsh conditions.
1. Shielding Against the Elements
Weather can be a thermal camera’s worst enemy. Rain, snow, and humidity can cause lens fogging and distort readings. If you’re working in wet conditions, consider using a waterproof cover or a sealed enclosure to protect the camera.
In extreme cold, acclimate the camera before use. Rapid temperature changes can cause condensation inside the device, which may affect performance or even cause permanent damage. A simple trick? Store the camera in an insulated case while moving between temperature extremes to allow gradual adjustment.
And in hot environments, avoid exposing the camera to direct sunlight for long periods. This can lead to overheating, affecting both accuracy and lifespan.
2. Keeping the Lens Clean
A dirty lens is one of the biggest culprits behind poor thermal images. Dust, dirt, and smudges can blur details, making it harder to detect temperature variations. In high-dust environments like construction sites or mining operations, regular cleaning is essential.
Use a soft, lint-free cloth to wipe the lens, and avoid harsh chemicals that could damage protective coatings. If your work involves chemical exposure, consider using a camera with a specialized protective coating.
Optimizing Camera Settings for Harsh Environments
Even the best camera won’t give accurate readings if it’s not configured correctly. Small adjustments can make a big difference in challenging conditions.
1. Adjusting Emissivity Settings
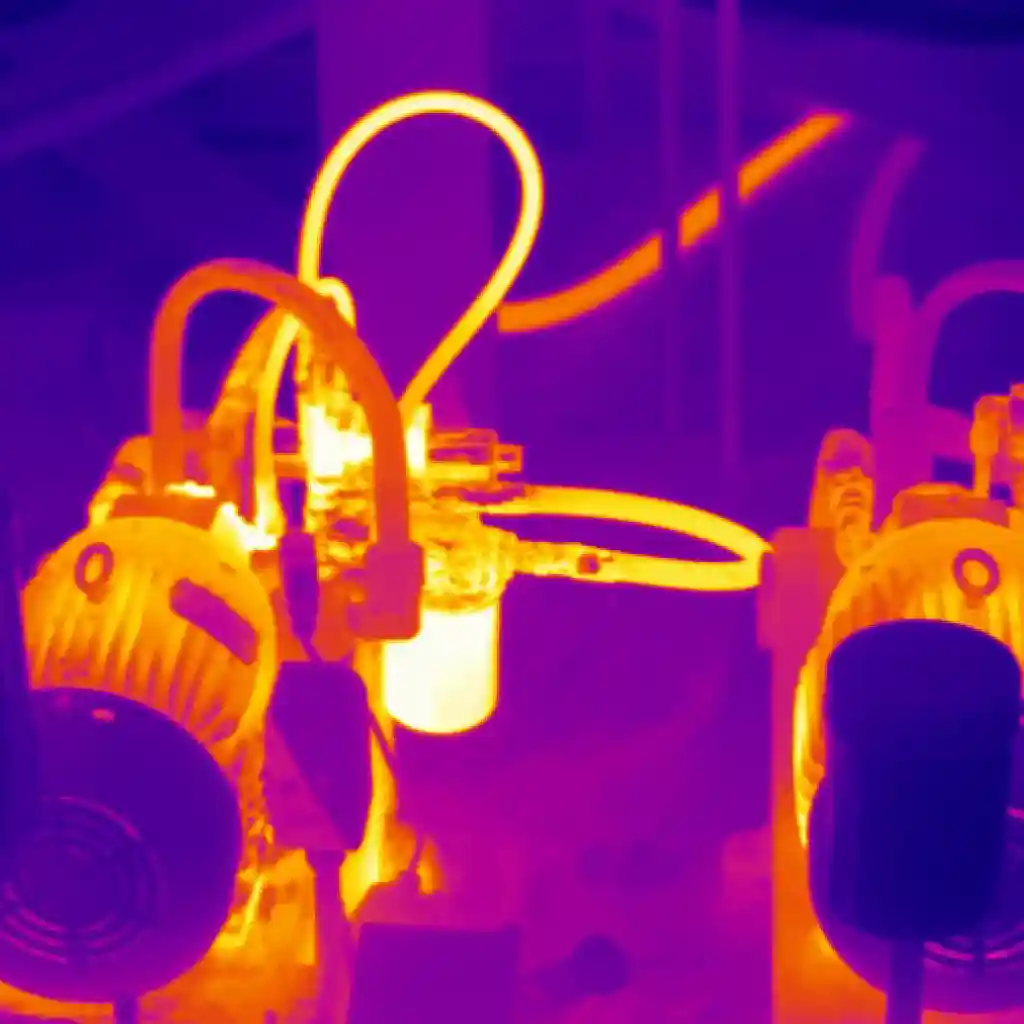
Every surface radiates heat differently, and adjusting the emissivity setting ensures your thermal camera reads temperatures accurately. This is especially important in industrial settings where materials like shiny metals reflect heat rather than emit it, leading to false readings.
2. Choosing the Right Color Palette
Different color palettes work better in different environments. For example:
- High-contrast palettes help when working in bright sunlight.
- Black-and-white modes are great for identifying subtle temperature differences in dusty conditions.
3. Using Noise Reduction in Foggy or Dusty Areas
If you’re working in a foggy or smoke-filled environment, some cameras offer noise reduction features to improve image clarity. Activating these settings can help filter out visual interference and enhance accuracy.
Training and Safety: Why the Right Knowledge Matters
Having the best camera won’t help if the person using it isn’t properly trained. Thermal imaging requires expertise, and in extreme environments, safety is just as important as accuracy.
1. Hands-On Training is Essential
New operators should receive hands-on training to understand how different environments impact thermal readings. They need to know how to handle the camera properly, interpret results, and troubleshoot common issues.
2. Establishing Clear Safety Protocols
In hazardous environments, using thermal cameras may involve working in dangerous areas—like inspecting pipelines in a gas plant or scanning electrical equipment in a high-voltage zone. Establishing clear safety protocols ensures operators stay out of harm’s way while capturing accurate data.
3. Using Protective Gear
Operators should always wear personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, helmets, and protective eyewear, especially in extreme industrial or military applications.
Leveraging Software for Better Thermal Analysis
Modern thermal cameras do more than just capture images—they come with advanced software to enhance analysis.
1. AI-Powered Fault Detection
Many high-end cameras use artificial intelligence to automatically detect faults, such as overheating components in electrical panels. This reduces human error and speeds up diagnostics.
2. Cloud-Based Reporting for Remote Monitoring
For industries that require continuous monitoring—like oil and gas or power plants—thermal data can be uploaded to the cloud for real-time analysis. This allows experts to monitor conditions remotely and take action before problems escalate.
Mastering Thermal Imaging in Extreme Conditions
Thermal imaging is a game-changer in industries that operate in extreme conditions, but to truly harness its potential, you need the right approach. Choosing a camera built for harsh environments, keeping it clean and well-maintained, optimizing its settings, and ensuring proper training all contribute to accurate results and equipment longevity.
When used correctly, thermal imaging doesn’t just enhance efficiency—it prevents costly failures, improves safety, and helps industries thrive in even the toughest conditions.
By following these best practices, you can make the most of thermal imaging technology no matter where your work takes you.